What is Competency Mapping & Framework? How To Do Competency Mapping?
Every individual and employee is unique and it’s also true with modern organizations. It is very important for the overall organizational success that we identify key skills required by its people to succeed in the ever-changing market environment. Competency mapping is one such technique that makes use of a more systematic and organized approach to define key behaviors that will lead to organizational or project success.
To be honest, it’s not easy to scientifically or objectively define behaviors, that’s where competency mapping proves to be such a powerful tool in the hands of the human resource and key stakeholders within the organization. We will cover the applications of competency mapping, the process of doing competency mapping and developing a competency framework, and how to interpret competency profiles.
What is the meaning of Competency Mapping?

At the forefront, the modern HR professionals have a job that every employee performs to the best of their abilities by identifying a role that is best suited for them. This matching of jobs and people to facilitate excellence in performance can be achieved through competency mapping.
Moreover, it is very important that each competency is defined properly with the use of the competency definition that makes it very clear what these competencies mean. Also, what all behaviors the employee needs to demonstrate (called Behavioral Indicators or BI) that would allow us to ascertain that the concerned employee possesses these skills in varying degrees (called Proficiency Levels or PI).
This essentially standardizes the process so that anyone looking at the competency framework developed through the competency mapping exercise can interpret it easily.
This standardization is extremely important as the competency mapping is at the heart of the human resource development of an organization. In this post, we will be covering all the aspects of competency mapping with the actual competency mapping method and the entire process of developing the competency framework and its application.
Competency is your ability to do something successfully or efficiently. Therefore, competency mapping is simply a process of matching your competence with the job role and/or organization. Additionally, it is also about matching people to the job role and hence used even in selection, training, and appraisals.
The Definition of Competency Mapping
Competency mapping is the process of identifying the specific skills, knowledge, abilities, and behaviors required to operate effectively in a specific job or organization. Competency maps are often also referred to as competency profiles or skills profiles.
There are multiple applications of Competency Mapping
Some of the major practical applications of competency mapping include
1. Job Evaluation
By analyzing the key skills to required to do a job a simple job evaluation can be prepared. It can help in allocating existing or new resources to the specific job based on the evaluation process
2. Project Planning
What key tasks can be performed by what resources in the project can easily be identified through the competency mapping process and helps in project planning.
3. Performance Management
A competency mapping exercise results in preparing Competency Framework, which in turn helps in allocating desired proficiency for the job vs current proficiency to do the job. By analyzing any gaps the performance management can be seamlessly conducted
4. Job Analysis
By identifying the key behaviors required to perform each job role, competency mapping is really useful in preparing job analysis. Not to be confused by Job description step in competency mapping process where the job roles analyzed for allocating competencies and behaviors.
5. Succession Planning
The analysis of competencies required for a leadership role and mapping them with proficiency shown by potential leaders a clear roadmap for succession planning can be created.
Any developmental need can also be ascertained by mapping the critical competencies with the current proficiency level demonstrated by an individual vis-à-vis the required proficiency level for the position.
6. Recruitment
By identifying key skills required to do the job and also developing a competency-based interviewing process the organizations can benefit by hiring the most suitable resources while it helps in all stages of the recruitment process.
7. Individual Development Plan
Any gaps in desired and current proficiency levels help in developing individual development plans and learning roadmap for individuals and even job roles and categories.
Understanding key steps of the Competency Mapping process
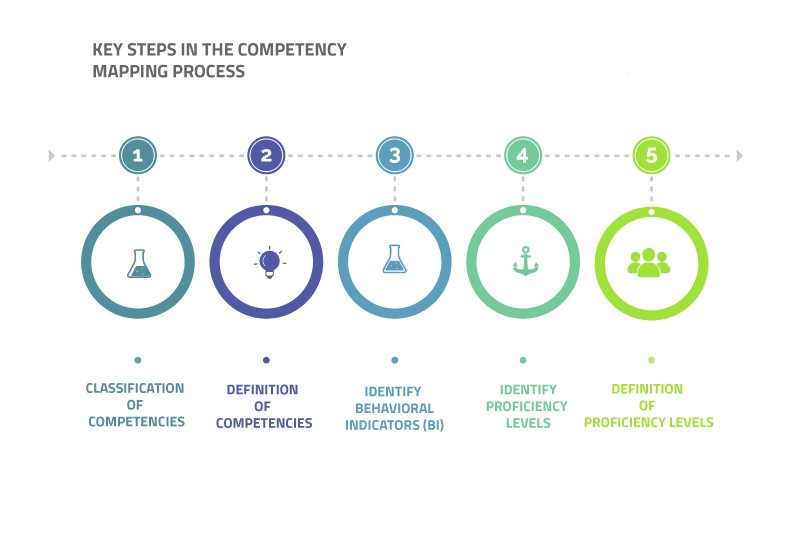
There are 5 key steps in any competency mapping process
These are not simply the steps but also the construct of the competency map. Each one of the step also from the elements in the competency map that you develop into a framework.
1. Classification of Competencies
Generally, the competencies are classified into two categories. Functional and Behavioral. However, the competency can be classified into more categories depending on the overall objective of developing a competency framework through the process of competency mapping.
For example, an organization that has decided to focus on enhancing customer experience may classify a category of competency as Customer Centricity.
2. Definition of Competencies
It is very important that competency is defined well. This helps in providing a clear picture of what exactly is the detail about the set of skills and abilities required to do the job. You can see the below example, where for a sales team the competency has been classified as functional and it has been clearly defined.
| FUNCTIONAL COMPETENCY | DEFINITION |
| Drive for Sales Results | The ability to achieve results by focusing on the formulated sales objectives |
Please note that it is not necessary that the mentioned competency ‘Drive for Sales Result’ will always be a functional competency. It may very well be a behavioral competency for other organizations. Still, competencies like ‘Knowledge in advanced MS Excel’ is clearly a functional competency and are easier to identify.
3. Identifying Behavioral Indicators (BI)
The key element of any competency mapping process and developing a competency framework is the set of behaviors that defines that competency. In the above example, we have already classified the competency as functional. Also, we have defined the competency, now the behavioral indicators will be assigned.
It typically says that you need to demonstrate these behaviors to show that you have the competency of ‘Drive for Sales Results’. Behavioral indicators are also called Behavioral Descriptors (BD) or simply BI, so don’t get confused is you see any other way BI is mentioned.
| FUNCTIONAL COMPETENCY | DEFINITION | BEHAVIORAL DESCRIPTOR(S) |
| Drive for Sales Results | The ability to achieve results by focusing on the formulated sales objectives | A. Establishes personal sales objectives that are Highlighted clearly, Ambitious, Realistic, and Directly applicable (HARD) B. Is proactive and takes the required initiatives to achieve personal sales objectives C. Can identify the concrete results of the sales activities undertaken D. Takes personal responsibility for achieving sales goals E. Monitors the progress of own sales results F. Thinks out of the box to achieve sales goals G. Is able to manage and overcome objections and resistance from other departments H. Helps Sames Managers to sell into key outlets |
Well, that looks like a detailed listing of behavioral indicators for the competency ‘Drive for Sales Results’ and provides a very clear-cut understanding to the individual, manager, and his/her HR team about what constitutes ‘Drive for Sales Results’ for an employee.
4. Identifying Proficiency Levels (PL)
Not every person in a department will be at the same level of expertise or in the context of competency mapping, at the same level of proficiency. Therefore, it is critical that within a job role, department, level or grade of employees the desired proficiency levels are defined.
Notice the term ‘desired’, in the competency mapping process the proficiency levels are desired proficiency levels (DPL) as at this moment you don’t know what proficiency levels your employees actually are.
Once you assess and measure proficiency levels then you would arrive at actual proficiency levels (APL). We have added the DFL for Level 2 managers in salesforce to give you an insight. A scale of 1 to 5 is used where 5 is the maximum level of proficiency as 1 is the minimum.
| FUNCTIONAL COMPETENCY | DEFINITION | BEHAVIORAL DESCRIPTOR(S) | DPL |
| Drive for Sales Results | The ability to achieve results by focusing on the formulated sales objectives | A. establishes personal sales objectives that are Highlighted clearly, Ambitious, Realistic, and Directly applicable (HARD). B. is proactive and takes the required initiatives to achieve personal sales objectives. C. can identify concrete results of the sales activities undertaken. D. takes personal responsibility for achieving sales goals. E. monitors the progress of own sales results. F. Thinks out of the box to achieve sales goals. G. Is able to manage and overcome objections and resistance from other departments H. Helps Sames Managers to sell into key outlets |
3 |
5. Definition of Proficiency Levels
As seen in the example above, we have a DPL of 3 that is just two below the maximum. But we do not know what would define a DPL of 4l. Therefore, it is extremely important that we clearly define the meaning of each level of proficiency from 1 to level 5 in DPL.
| Proficiency Level | Meaning |
| Level 1 = Novice | Is struggling in demonstrating relevant behaviors of competency |
| Level 2 = Learner | Knows and understand, however, may commit mistakes in applying sometimes |
| Level 3 = Practitioner | Knows, Understands and applies with a fair degree of consistency |
| Level 4 = Expert | Knows, Understands and applies and innovates with a fair degree of consistency |
| Level 5 = Master | Role model a competency, often quoted when looking for a standard, can coach others |
Pretty simple and objective, isn’t it? You have just seen the competency mapping process in real-time for a real organization by going through an example of one competency being mapped, in this case to one job role.
 |
| The competency mapping and development of Competency Framework is mostly done by Job Roles. For example, a customer service executive, team leader, and manager will have different competency profiles. It can also be done department wise like sales, customer service, marketing, production, etc.
In recent times many organizations have also been developing Competency Framework for the entire whole organization where they identify 4 to 6 competencies for the entire organization. The Behavioral Indicators (BI) also remain the same across roles and function but proficiency levels vary based on the tenure, seniority or role of the employee. |
Methods of Competency Mapping

Job and Role Analysis
This is the most crucial stage in competency mapping. In this stage, the job that the employee needs to perform is critically analyzed and this is broken down into four stages. This stage can also include a competency-based questionnaire to find out the following.
- Tasks the employee needs to perform
- Behaviors that he or she need to demonstrate to achieve these tasks
- Behavioral indicators that would lead us to ascertain that these behaviors are being demonstrated
- Defining proficiency for each behavior
Let us take understand by an example. If we are doing competency mapping for a job role of team leader for a software development firm. One task that a team leader has to perform is to ensure the productivity of all his team members. Accountability towards the team results and ensuring the productivity of each individual in the team is the behavior that he or she needs to demonstrate.
Now we may identify behaviors that would lead to the productivity of the employees. The behaviors that would lead to this competency can be his or her ability to set goals, ability to provide direction, ability to coach and so on. This is the identification of indicators that would lead to the final behavior and thus are called behavioral indicators.
Interview
It involves face to face interaction to determine and fine-tune behaviors and behavioral indicators. The interview at this stage can involve the individual already in the job role, his or her supervisor, HoD or even the project manager in case of projects.
Develop a Competency-based job description (JD)

A competency-based job description is then arrived at. For e.g in case of the team leader, the job description will mention all the behaviors required to be successful in the job role. It can include accountability for productivity, the efficiency of work, quality of work, adherence to timelines and more.
Map the competencies
In this stage mapping the competencies and behaviors to the job role happen. Also in this stage, the proficiency for each role is also determined. For e.g a team leader has to have a proficiency of 3 out of 5 for ensuring the productivity of his or her employees. A top leader may need to exhibit a proficiency of 4.5 out of 5 for the same.
Look how competencies and behaviors may remain the same but proficiency may vary across various levels in the organization.
Identify critical competencies for further development

Identifying critical and key competencies can help create detailed role directories that can guide organizations when making hiring or promotion decisions specific to that position.
In the present economic environment, employee performance is a primary concern of HR managers and the best way to recognize performance is to observe key characteristics of high performing employees that distinguish them from less productive employees.
SOME OF THE TOOLS USED FOR COMPETENCY MAPPING
- INTERVIEWS
- COMPETENCY-BASED QUESTIONNAIRES
- ASSESSMENT AND DEVELOPMENT CENTERS
- CRITICAL INCIDENTS TECHNIQUE
- PSYCHOMETRIC TESTS
Conclusion
Not only does Competency mapping help in the Appraisal process, but as mentioned above, it helps in hiring the right talent through better filtering of the core competencies required for the job and eliminating the unqualified candidates.
Furthermore, it helps in shortening the recruitment cycle by getting only those candidates who possess the skills as mentioned in the framework and putting them in the right department from day one to ensure the efficiency and effectiveness are maintained.
Overall, the necessity of a Competency Framework is a must for every organization, but it is with the support of the management that its effectiveness can be rightly put in place.

